Sugar is a widely used crystal that makes our lives sweet. Sugar crystal can be colorless, white, or brownish depending on its refining state. Refined sugar is mostly colorless or white whereas less refined sugar tends towards brownish color.
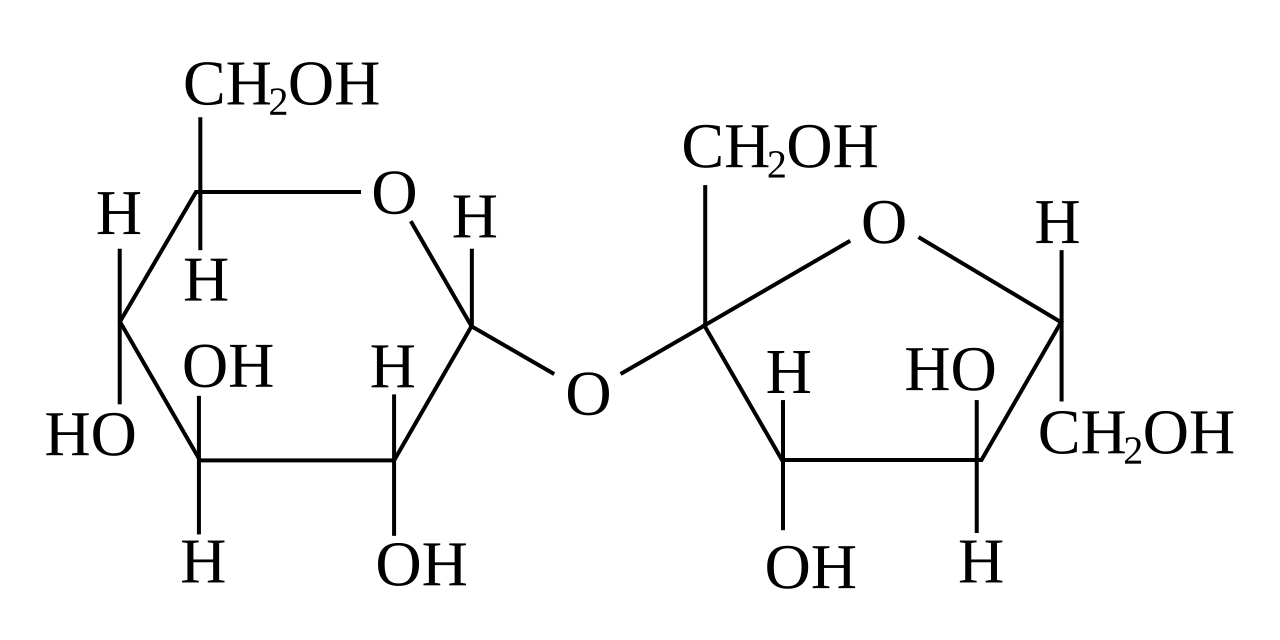
Chemically Sugar is Saccharides, a form of Carbohydrates. The sugar we use on daily basis refers to Sucrose, a Disaccharide. Disaccharides are formed when two Monosaccharides (Glucose, Fructose and Galactose) are bonded together by Glycosidic bonding. Monosaccharides are commonly known as Simple Sugar whereas Disaccharides are called Compound Sugar. Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides are formed from the polymerization of multiple Monosaccharides and have a longer chain. They are not considered Sugar.
In a nutshell, Sucrose is the chemical name of Sugar. And it is abundant in nature. Fruits, Vegetables and Plants contains sugar in them through photosynthesis. The sugar we see in our day-to-day use, is the crystalline form such sucrose from sugarcane or sugar beets. Sugarcane and Sugar Beets contain highest amount of sugar, and this makes it economical options for sugar manufacturing.
Sugar Molecule
From previous discussion, it is clear that Sugar is a Disaccharide (Sucrose). What are Monosaccharides then? Glucose, Fructose and Galactose are Monosaccharides. If we compare Carbohydrates with a wall, these three Monosaccharides are the smallest block like bricks of the wall.
Glucose and Fructose are formed naturally in plants, vegetables and fruits. Unlike previous two Monosaccharides, Galactose does not have a free form, but it is a constituent with glucose of the disaccharide lactose (milk sugar).
Monosaccharides
- Sucrose (Glucose + Fructose)
- Lactose/Milk Sugar (Glucose + Galactose)
- Maltose (2 Glucose)
Polysaccharides are not considered as Sugar as I previously mentioned. So I kept this aside from this discussions. We consume Polysaccharides like starch everyday. Our body converts these into consumables Monosaccharides.
So, Sugar is simply a Carbohydrate.

Comments
Post a Comment